The Dual Identity of Cashew - Fruit and Nut Explained
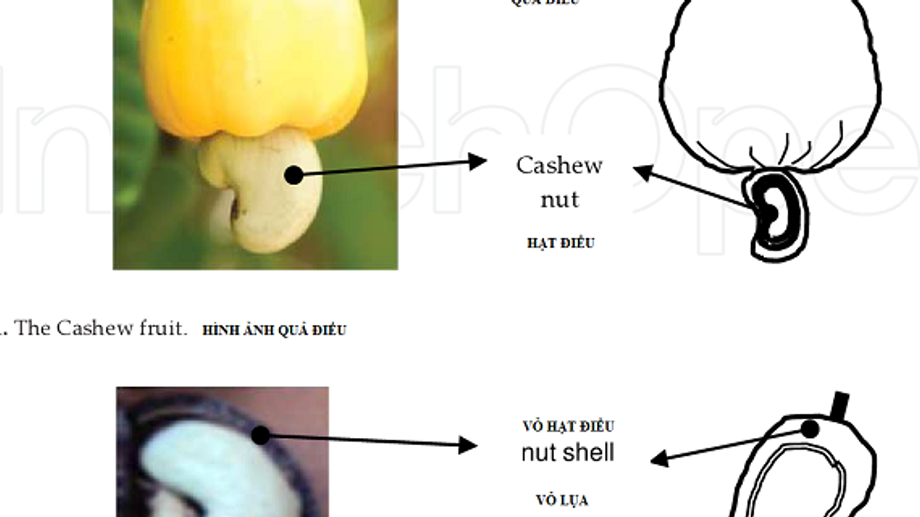
1. Cashew is a fruit or seed
Cashew is actually both! The cashew tree produces two distinct parts: the cashew apple and the cashew nut.
- Cashew Apple: This is the fleshy, pear-shaped structure that grows on the tree. It's technically the swollen stem and is edible. People often use it to make juices, jams, or even alcoholic beverages.
- Cashew Nut: This is the true seed of the cashew tree, found at the bottom of the cashew apple. It's encased in a hard shell that contains toxic oil, which is why cashew nuts are always sold shelled.
So, when you enjoy cashews, you're actually eating the seed of the cashew fruit.
2. Full explanation about cashew fruit
The cashew fruit is quite unique and fascinating. Here's everything you need to know about it:
Structure of the Cashew Fruit
- Cashew Apple: This is the swollen stem of the cashew tree. It has a juicy, fibrous, and pear-shaped body, usually yellow or red. Despite its name, the cashew apple is not a true fruit but is often referred to as one due to its appearance and juicy nature. It is edible and can be consumed fresh, juiced, or used to make alcoholic beverages like feni in Goa, India.
- Cashew Nut: This is the true fruit of the cashew tree, located at the bottom of the cashew apple. The nut is encased in a hard shell that contains a toxic oil called urushiol, which can cause skin irritation. This is why cashews are never sold in their shells.
Uses of the Cashew Fruit
Cashew Apple:
- Culinary Uses: The cashew apple is eaten fresh in some cultures, but its high tannin content can make it a bit astringent. It is more commonly used to make juices, jams, chutneys, and alcoholic beverages.
- Health Benefits: It is rich in vitamin C, calcium, and other nutrients, making it a nutritious snack.
- Cashew Nut:
- Culinary Uses: The nut is the most valued part of the cashew fruit. After removing the toxic shell through roasting or steaming, the nuts are consumed raw, roasted, or used in various recipes. Cashew nuts are popular in confectioneries, cooking, and as a standalone snack.
- Health Benefits: Cashews are packed with nutrients, including healthy fats, proteins, vitamins, and minerals. They are beneficial for heart health, bone strength, and weight management.
Processing the Cashew Nut
The processing of cashew nuts is labor-intensive due to the toxic shell. Here are the steps:
- Harvesting: The cashew apples are collected from the trees.
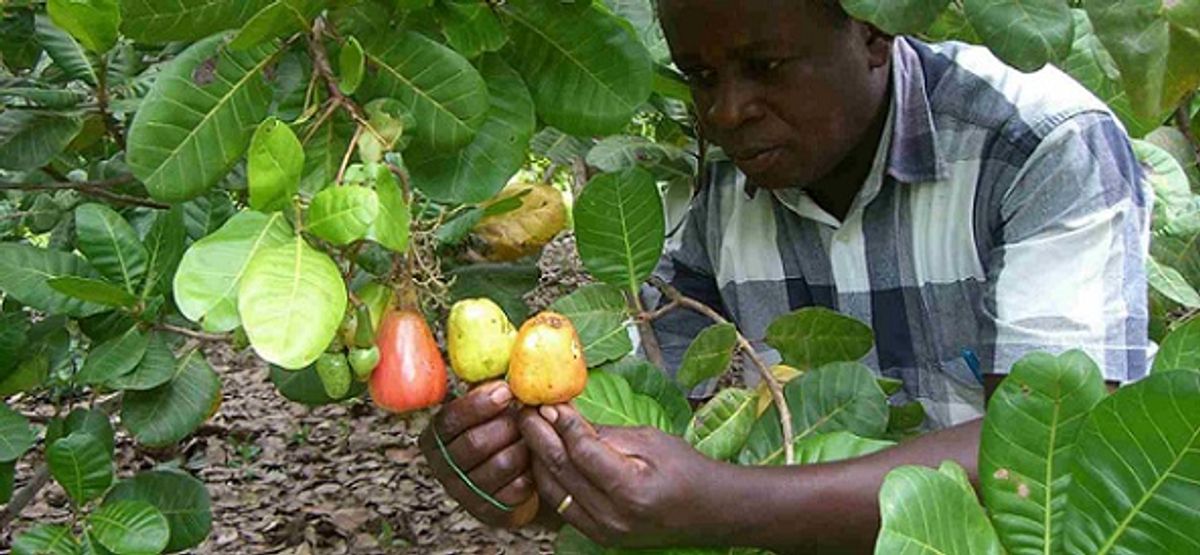

- Separation: The nut is separated from the apple.
- Roasting/Steaming: The nuts are roasted or steamed to soften the shells and neutralize the urushiol.
- Shelling: The shells are then removed, either manually or with machinery, to extract the kernel.
- Peeling: The thin, inner skin of the nut is peeled away.
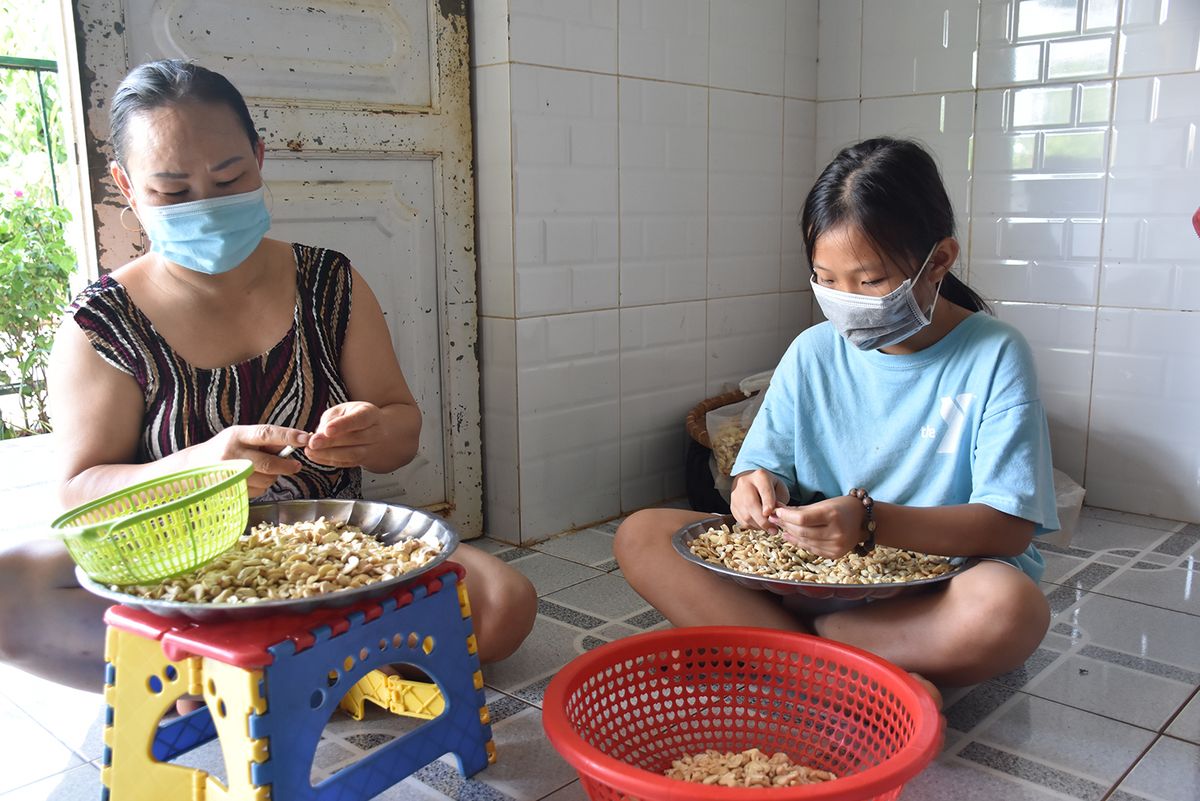

- Drying: The kernels are dried to reduce moisture content and enhance shelf life.
- Grading: The cashews are graded based on size and quality before packaging.
Economic Importance
- Cashew trees are primarily grown in tropical regions, with significant production in countries like India, Vietnam, Nigeria, and Brazil. The cashew industry supports the livelihoods of millions of farmers and workers in these regions. Cashew products, including nuts and derivatives like cashew butter, cashew milk, and cashew oil, have high economic value.
Fun Facts
- The cashew tree (Anacardium occidentale) is native to Brazil.
- The term "cashew" derives from the Portuguese word "caju," which comes from the indigenous Tupi name "acajú."
This unique combination of a juicy apple and a nut packed with nutrition makes the cashew fruit a remarkable and versatile food source.
3. Nutritional composition of cashew fruit
The cashew fruit, including both the cashew apple and the cashew nut, is packed with nutrients. Here's a detailed breakdown of its nutritional composition:
Cashew Apple (per 100 grams)
- Energy: 70 kcal
- Protein: 0.84 g
- Fat: 0.30 g
- Carbohydrates: 14.3 g
- Fiber: 0.9 g
- Sugars: 9.2 g
- Vitamin C: 0.6 mg
- Calcium: 8 mg
- Iron: 0.6 mg
- Magnesium: 21 mg
- Potassium: 250 mg
Health Benefits
- Heart Health: Cashews are rich in heart-healthy monounsaturated fats and omega-3 fatty acids.
- Bone Health: High in magnesium and phosphorus, which are essential for bone health.
- Energy Production: Contains copper and manganese, which are important for energy production and brain health.
- Immune System: Vitamin C and other antioxidants help boost the immune system.
- Digestive Health: The fiber content aids in digestion and promotes a healthy gut.
Cashew fruit is not only delicious but also offers a wide range of health benefits. Whether you enjoy the juicy cashew apple or the crunchy cashew nut, you're getting a nutritious snack!
4. Full explanation about cashews
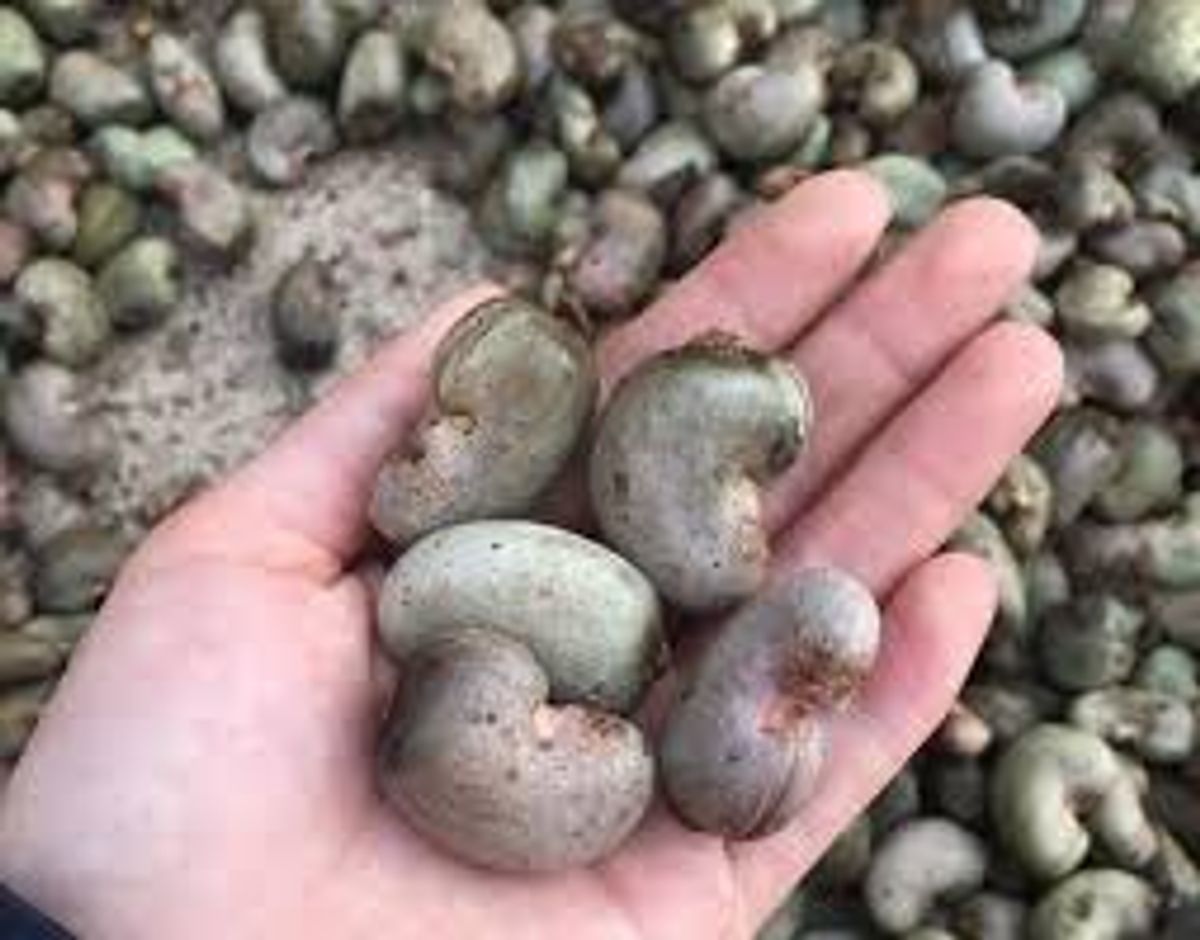

Cashews are the seeds of the cashew tree (Anacardium occidentale), a tropical evergreen tree native to Brazil. They grow at the bottom of the cashew apple, which is the swollen stem of the tree.
Structure of Cashews
Cashew Apple:
- Appearance: Pear-shaped, typically yellow or red.
- Taste: Juicy and sweet, but with a slightly astringent taste.
- Uses: Eaten fresh, made into juices, jams, chutneys, and alcoholic beverages like feni in Goa, India.
Cashew Nut:
- Appearance: Kidney-shaped, encased in a hard shell that contains toxic oil.
- Uses: Consumed raw, roasted, or used in recipes. Popular in confectioneries, cooking, and as snacks.
Nutritional Composition
Cashew Apple (per 100 grams):
- Calories: 70 kcal
- Protein: 0.84 g
- Fat: 0.30 g
- Carbohydrates: 14.3 g
- Vitamin C: High
Cashew Nut (per 28 grams):
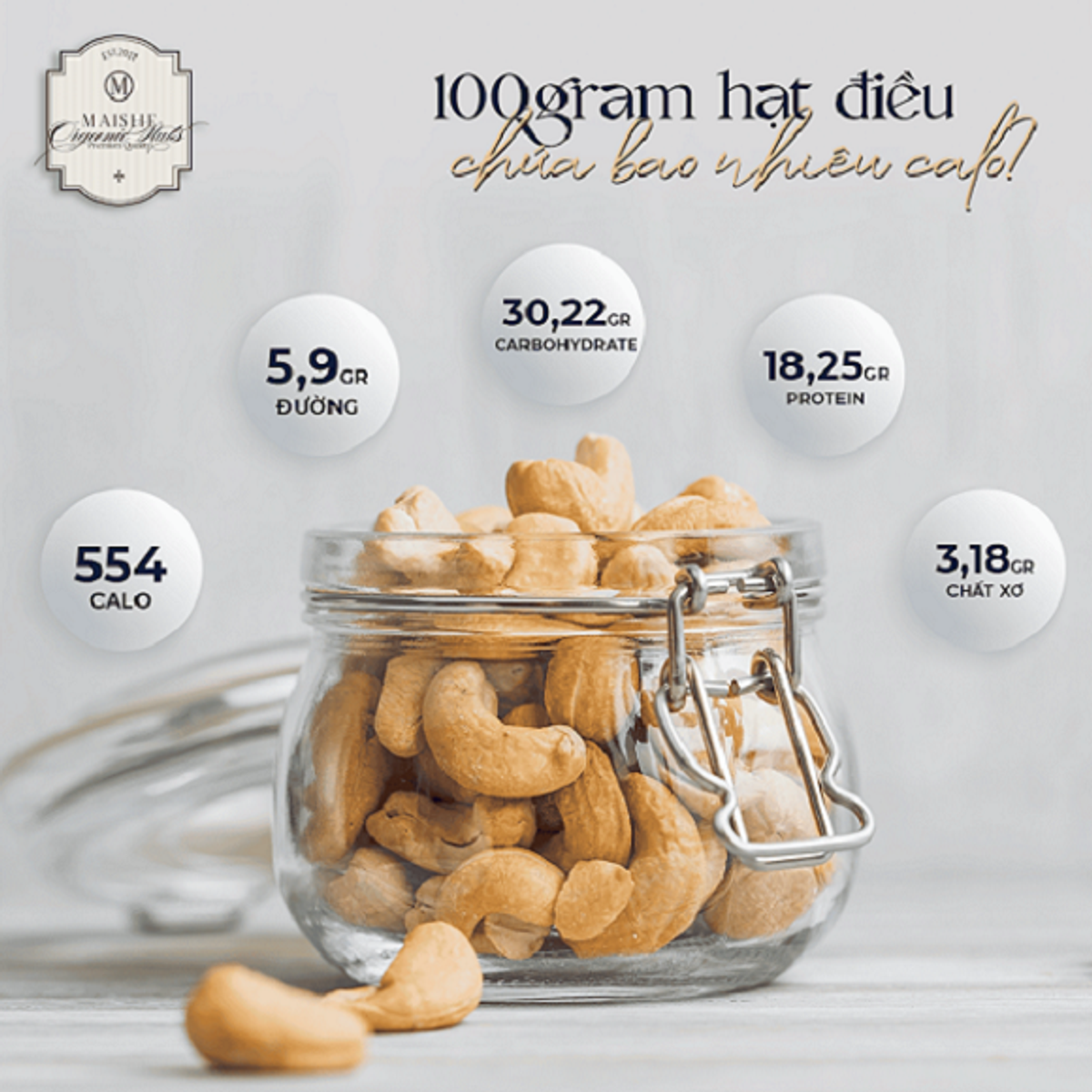
- Calories: 156 kcal
- Protein: 5.17 g
- Fat: 12.43 g
- Carbohydrates: 8.56 g
- Vitamins: K, B6
- Minerals: Magnesium, Iron, Zinc, Phosphorus
Health Benefits
- Heart Health: Rich in heart-healthy monounsaturated fats and omega-3 fatty acids. Bone Health: High in magnesium and phosphorus. Energy Production: Contains copper and manganese. Immune System: Boosts with vitamin C and antioxidants. Digestive Health: Aids digestion with fiber content.
Processing of Cashew Nuts
- Harvesting: Cashew apples are collected.
- Separation: The nut is separated from the apple.
- Roasting/Steaming: Nuts are roasted or steamed to neutralize urushiol oil.
- Shelling: Shells are removed to extract the kernel.
- Peeling: The thin inner skin is peeled away.
- Drying: Kernels are dried to reduce moisture content.
- Grading: Cashews are graded based on size and quality before packaging.
Economic Importance
- Cashew trees are primarily grown in tropical regions, with significant production in countries like India, Vietnam, Nigeria, and Brazil. The cashew industry supports the livelihoods of millions of farmers and workers. Cashew products have high economic value.
Fun Facts
- The term "cashew" derives from the Portuguese word "caju."
- Cashew nuts are never sold in their shells due to the toxic oil they contain.
Conclusion
Cashews are a versatile and nutritious food source, enjoyed worldwide in various forms. Whether it's the juicy cashew apple or the crunchy cashew nut, this remarkable fruit offers numerous culinary and health benefits.
5. Nutritional composition of cashew nuts
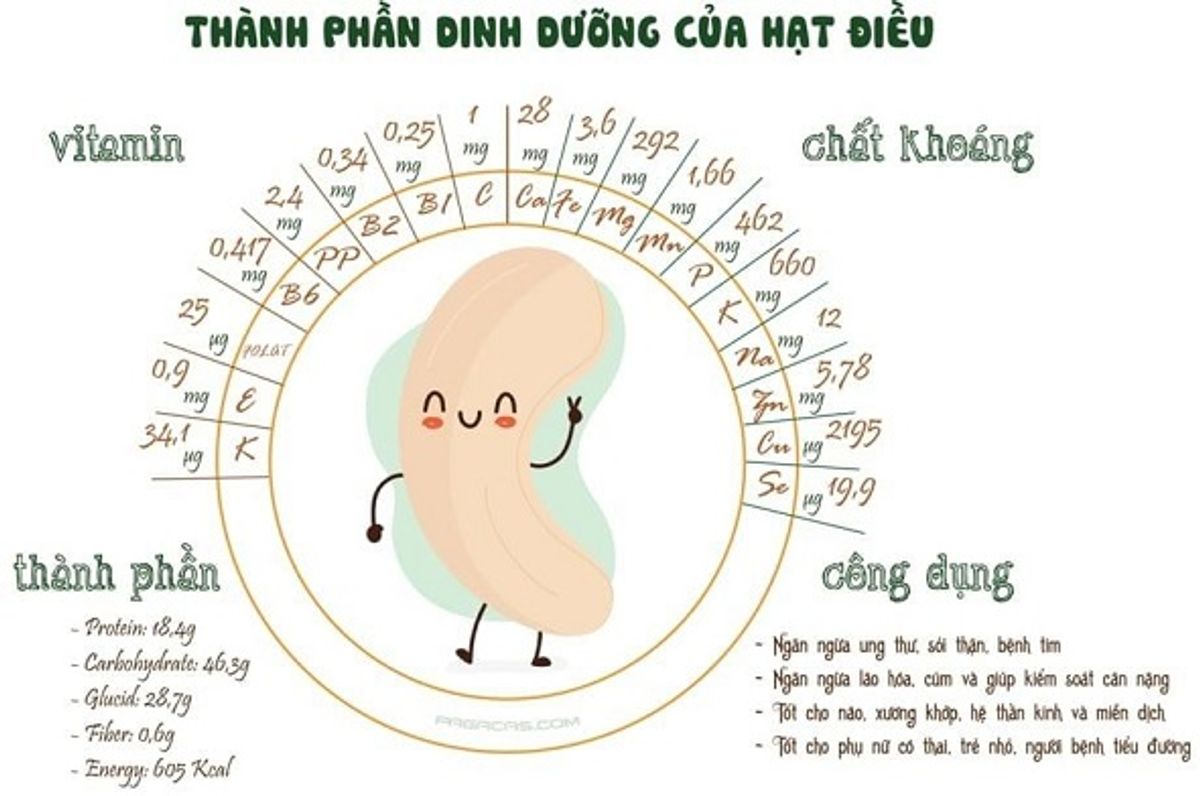
Cashew nuts are a nutrient-dense food, offering a variety of essential vitamins, minerals, and healthy fats. Here’s a detailed breakdown of their nutritional composition per 28 grams (approximately 1 ounce):
Calories
Energy: 156 kcal
Macronutrients
Carbohydrates: 8.56 g
- Fiber: 0.94 g
- Sugars: 1.68 g
Fats: 12.43 g
- Saturated Fat: 2.21 g
- Monounsaturated Fat: 6.75 g
- Polyunsaturated Fat: 2.22 g
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: 0.02 g
- Omega-6 Fatty Acids: 2.21 g
Protein: 5.17 g
Vitamins
- Vitamin K: 9.67 mcg
- Vitamin B6: 0.12 mg
Minerals
- Copper: 0.62 mg
- Manganese: 0.47 mg
- Magnesium: 82.78 mg
- Zinc: 1.64 mg
- Phosphorus: 168.11 mg
- Iron: 1.89 mg
- Selenium: 5.64 mcg
- Potassium: 187.11 mg
Other Nutrients
- Phytosterols: Beneficial plant compounds that help lower cholesterol levels.
- Antioxidants: Help protect the body against oxidative stress and inflammation.
Health Benefits
- Heart Health: Rich in heart-healthy monounsaturated fats and omega-3 fatty acids.
- Bone Health: High in magnesium and phosphorus, essential for strong bones.
- Energy Production: Contains copper and manganese, crucial for energy production and brain health.
- Immune System: Packed with zinc and selenium, which boost the immune system.
- Digestive Health: The fiber content aids in digestion and promotes a healthy gut.
Cashew nuts are not only delicious but also offer numerous health benefits, making them a valuable addition to a balanced diet.
Xem thêm: Điều là quả hay hạt? Giải thích đấy đủ về quả điều và hạt điều
Learn more: Are Cashews Seeds, Fruits or Nuts? Characteristics of Cashews & Cashew Nuts